5G Types: Fast to Faster to Fastest
May 7, 2021 Category: 5G Technologies
5G can be implemented in multiple ways, three of which are most prominent and are being targeted by the major operators in the United States. 5G speeds depend on the distance from the tower and it greatly reduces after 1km.

5G Speeds Based on Distance Away From Site
PCMag has another interesting scenario about 5G speeds when it conducted a live testing at Michigan Avenue in Chicago.
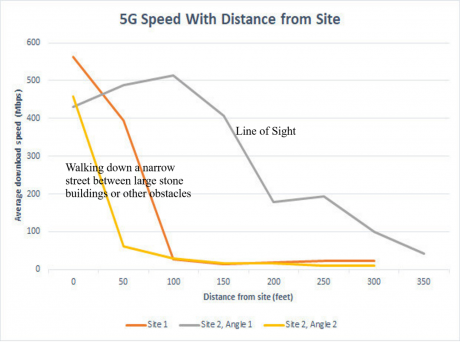
5G Speed With Distance From Site (Source: PCMag.com)
As shown above, the average download speed deteriorates to less than 50 Mbps when the distance from the site exceeds 50 to 100 feet (15m to 30m). This goes to show that multiple, low-height towers would likely be a mandatory requirement of 5G.
5G Types and Their Adopters
The four major US operators – AT&T, Verizon, T-Mobile and Sprint – have their own plans on building 5G networks for their customer bases. Their strategies are based on their existing wireless spectrum holdings as well as their future plans on fibre deployment to the tower which is necessary for building the fastest 5G type.
The following is a summary of 5G types and their adopters:
- mmWave high-band 5G: T-Mobile, AT&T and Verizon.
The high-band is about 10x faster than 4G LTE with extremely low latency, allowing individual messages to be transmitted almost instantaneously. However, the speed deteriorates rapidly as distance from the tower increases.
- Mid-band 5G: T-Mobile.
The mid-band is about 6x faster than 4G LTE. However, it has a smaller footprint than low-band.
- Low-band 5G: T-Mobile and AT&T.
The low-band is about 20 percent faster than 4G LTE.
These bands can also be illustrated in the following figure:
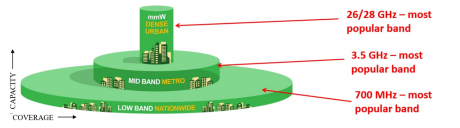
Typical 5G Frequency Bands (Source: Operator Watch Blog)
As shown above, the mmWave high-band which offers the highest capacity but lowest coverage is the most suitable for dense urban environments. The low-band which offers the widest coverage but lowest capacity is most suitable for rural coverage. The mid-band is in between the high-band and low-band in terms of capacity and coverage, and is suitable for metro environments.
Advantages of mmWave High-Band 5G
In a 4G network, a 4GB file download typically takes over 5 minutes (with a 100 Mbps connection). On a 5G network of mmWave high-band type, the same file would only take 32 seconds (with a 1Gbps connection). However, according to PCMag, this speed can only be achieved if the distance from the tower is less than 80 feet (25m).
Another advantage of the mmWave high-band 5G is its extremely low latency. This feature is especially useful in self-driving cars and online gaming, where spontaneous response is mandatory.
However, the mmWave high-band 5G is being rolled out by operators in very limited areas such as stadiums, arenas and other highly dense areas. Most of the other rollouts will be of mid-band or low-band type, which provide reasonable coverage but not extremely fast speeds.
Key Takeaways
- As with most of the new technologies, there is a lot of hype surrounding 5G speeds. Although lightning speed is achievable, most of the users will get only a fraction of it as they move away from the tower.
- The three major cellular operators in the US have different plans regarding the deployment of 5G networks. However, some applications do not require long-distance communication.
- For example, for communication among the “connected cars”, the required reach is within a few meters. Perhaps more of such applications will be developed in the next few years. Necessity is the mother of invention.
Follow us on LinkedIn to stay tuned to our weekly updates of the latest developments in the Telecom/IT industry and popular courses that we offer.
Share this on…